
GAGs were originally called mucopolysaccharides, which is where this condition gets its name. The IDUA gene provides instructions for producing an enzyme that is involved in the breakdown of large sugar molecules called glycosaminoglycans (GAGs). Heart disease and airway obstruction are major causes of death in people with both types of MPS I. Some people with the attenuated type have learning disabilities, while others have no intellectual impairments. Individuals with attenuated MPS I typically live into adulthood and may or may not have a shortened lifespan. Children with this form of the disorder usually have a shortened lifespan, sometimes living only into late childhood. Developmental delay is usually present by age 1, and severely affected individuals eventually lose basic functional skills (developmentally regress). While both forms of MPS I can affect many different organs and tissues, people with severe MPS I experience a decline in intellectual function and a more rapid disease progression. Narrowing of the spinal canal ( spinal stenosis ) in the neck can compress and damage the spinal cord. Carpal tunnel syndrome develops in many children with this disorder and is characterized by numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hand and fingers.
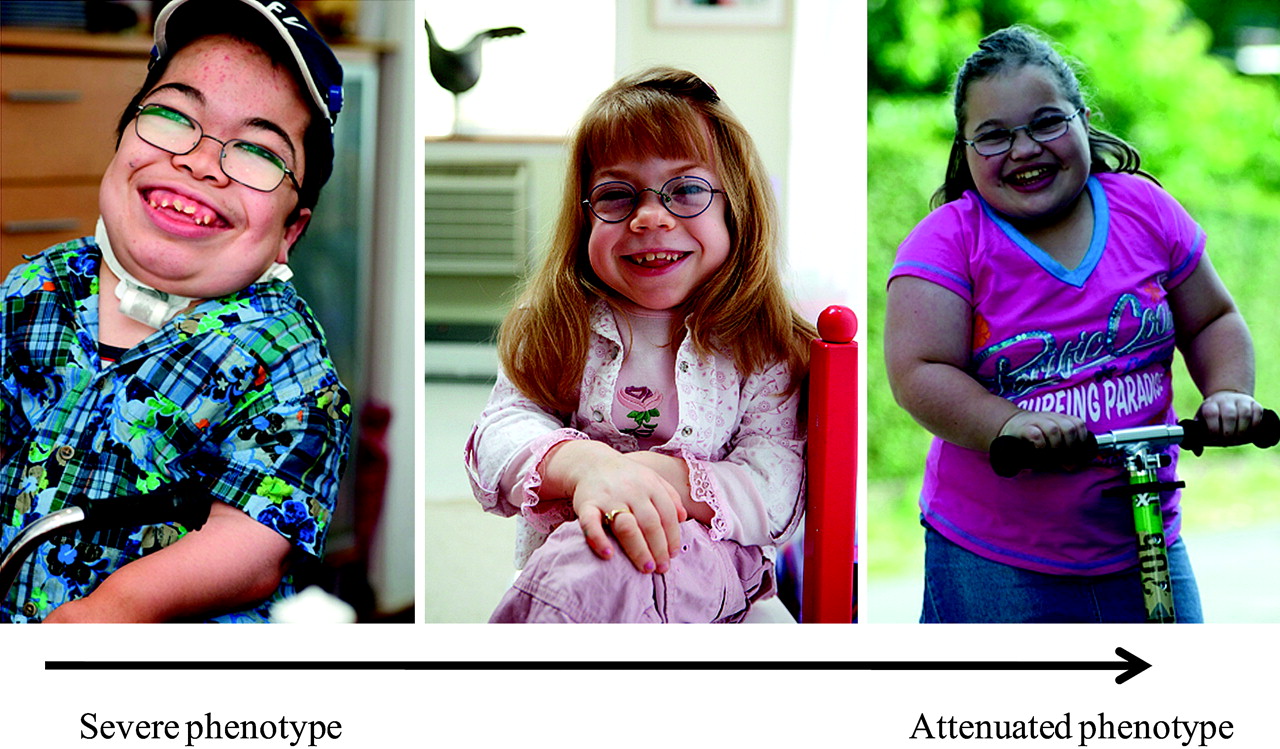
Most people with the severe form of the disorder also have dysostosis multiplex, which refers to multiple skeletal abnormalities seen on x-ray. Some individuals with MPS I have short stature and joint deformities (contractures) that affect mobility. Affected individuals may also have hearing loss and recurrent ear infections. People with MPS I often develop clouding of the clear covering of the eye ( cornea ), which can cause significant vision loss. The airway may become narrow in some people with MPS I, causing frequent upper respiratory infections and short pauses in breathing during sleep (sleep apnea). Vocal cords can also enlarge, resulting in a deep, hoarse voice. Individuals with MPS I may have a large head (macrocephaly), a buildup of fluid in the brain (hydrocephalus), heart valve abnormalities, distinctive-looking facial features that are described as "coarse," an enlarged liver and spleen (hepatosplenomegaly), and a large tongue (macroglossia). People with severe MPS I generally begin to show other signs and symptoms of the disorder within the first year of life, while those with the attenuated form have milder features that develop later in childhood. Because there is so much overlap between each of these three syndromes, MPS I is currently divided into the severe and attenuated types.Ĭhildren with MPS I often have no signs or symptoms of the condition at birth, although some have a soft out-pouching around the belly-button (umbilical hernia) or lower abdomen (inguinal hernia).

This disorder was once divided into three separate syndromes: Hurler syndrome (MPS I-H), Hurler-Scheie syndrome (MPS I-H/S), and Scheie syndrome (MPS I-S), listed from most to least severe. Mucopolysaccharidosis type I (MPS I) is a condition that affects many parts of the body.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
